Annual Summary of Disease Activity:
Disease Control Newsletter (DCN)
Related Topics
Contact Info
Babesiosis, 2019
Babesiosis is a malaria-like illness caused by a protozoan parasite, typically Babesia microti, which infects red blood cells. B. microti is transmitted to humans by bites from Ixodes scapularis (the blacklegged tick), the same vector that transmits the agents of Lyme disease, human anaplasmosis, one form of human ehrlichiosis, and a strain of Powassan virus. Babesia parasites can also be transmitted by blood transfusion. Although most people infected with Babesia have asymptomatic infections, people with weak immune systems, other co-morbidities, and the elderly can become seriously ill.
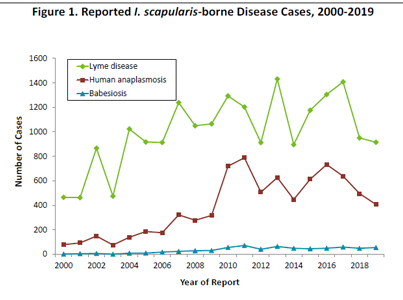
In 2019, there were 55 confirmed and probable cases reported (0.97 cases per 100,000), a slight increase from the 49 cases in 2018. Over the past decade, slight annual fluctuations in reported cases have been observed, however, reported case numbers continue to trend upward (range, 41 to 72) and are consistently higher than annual cases reported in the previous decade, 2000-2009 (range, 1 to 31) (Figure 1). In recent years, case demographics were similar. In 2019, 40 (73%) of the cases occurred in males. The median case age was 67 years (range, 4 to 97), up from 64 in 2018, and older than the median ages for both anaplasmosis (62 years) and Lyme disease (48 years). Illness onset dates peaked in the summer months: 40 (77%) of 52 cases with known onset date reported first experiencing symptoms in June, July, or August. Twenty- four (44%) cases were hospitalized due to their infection in 2018 with a median admission duration of 4 days (range, 2 to 10). Seven patients reported severe complications (e.g. organ failure), but there were no deaths attributed to babesiosis infection.
- Find up to date information at>> Babesiosis (Babesia microti)
- Full issue>> Annual Summary of Communicable Diseases Reported to the Minnesota Department of Health, 2019