Alcohol and Other Drugs
Alcohol Basics
Alcohol Data
Related Topics
What is a Drink of Alcohol?
Alcohol use impacts everyone whether you, or someone else, uses alcohol. It’s important to know and understand how much alcohol you are drinking to make the best decision for your health.
If you, or someone you know, need help with alcohol use disorder call SAMHSA’s National Helpline at 1-800-622-4357, or talk with your health care provider.
The standard drink
A standard drink is 0.6 ounces of pure alcohol. The picture below helps visualize how “one drink” looks across beverage types. Alcoholic drinks vary in types, sizes, and alcohol content. Similarly, the way alcohol affects the body will differ from person to person. While these are standard definitions of a drink, the amount of alcohol in a drink can be different if not measured appropriately. For example, beverage servers may provide drinks with more or less alcohol in them. It is important to be aware of what you are drinking, and understand that one beer or one cocktail may not equal one standard ‘drink’.
If someone chooses to drink alcohol, the 2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends that you do so in moderation. Learn more CDC- About Standard Drink Sizes.
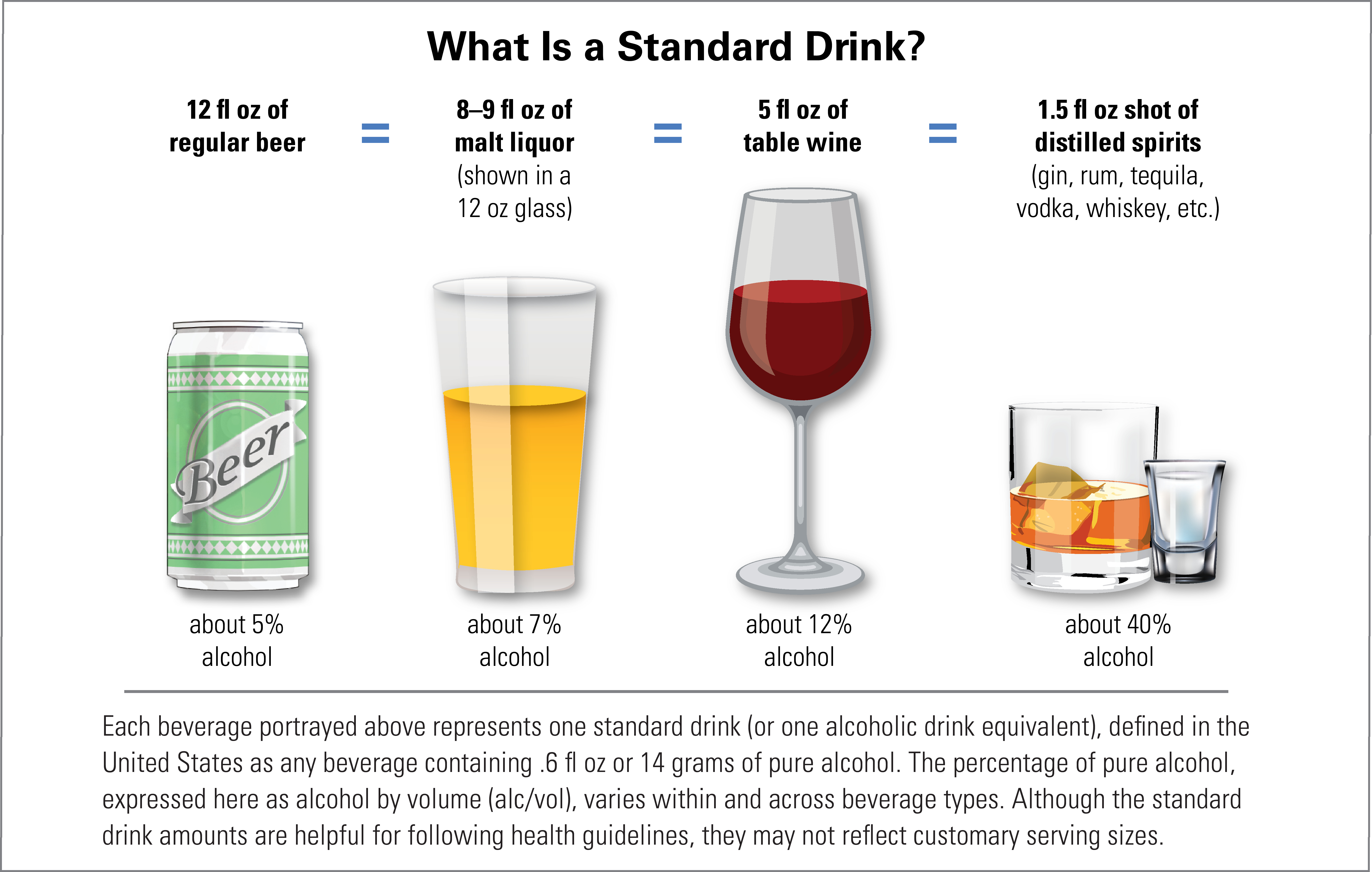
Source: National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism
Moderate, binge, heavy and excessive drinking
How much, and how often, and how fast a person drinks alcohol can be categorized into different levels. These levels are helpful in evaluating your own risk or another person’s risk for alcohol-related harms. Emerging research suggests that there is no level of alcohol use that carries no risk, so the healthiest decision is to not drink alcohol.
Moderate drinking
The U.S. Dietary Guidelines for Americans define moderate drinking as one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men, among legal drinking-aged adults.
Excessive drinking
Excessive drinking includes binge drinking, heavy drinking, any drinking by pregnant women, and any alcohol use by people under age 21.
Binge drinking is excessive drinking
Binge drinking is a drinking pattern that roughly brings a person’s blood alcohol concentration (BAC) to 0.08 grams percent or above. That is about four or more drinks on one occasion for women, or five or more drinks for men in the span of about two hours (1). Binge drinking is associated with increased risk for unintentional injuries, violence, chronic diseases, cancer, and alcohol dependence (1).
Quick facts on binge drinking in Minnesota
Heavy drinking is excessive drinking
Heavy drinking is defined as consuming 8 or more drinks per week for women, or 15 or more drinks per week for men.
Alcohol use during pregnancy is excessive drinking
Drinking alcohol while pregnant puts the baby at risk for lifelong physical, educational, behavioral and emotional problems. Visit Alcohol and Your Health to learn why pregnant women should not drink alcohol.
Underage drinking is excessive drinking
Youth who start using alcohol before the age of 15 are four times as likely to become alcohol dependent than those who do not start until they are 21 (2). Youth who drink during high school are more likely to (3):
- Experience academic problems like low grades or school absences
- Engage in risky sexual behaviors such as unprotected sex
- Be involved in physical fights
- Use tobacco or other drugs including marijuana, cocaine, or inhalants
- Seriously consider attempting or attempt suicide
Data brief on youth and underage drinking in Minnesota (PDF)
For more information
Kari Gloppen at kari.gloppen@state.mn.us or Kathleen Dubberley at kathleen.dubberley@state.mn.us for alcohol-related data, policy, or program information.
Citations
(1) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2018). Alcohol Use and Your Health.
(2) Dawson D, RB G, Chou S, Ruan W, Grant B. Age at first drink and the first incidence of adult-onset DSM-IV alcohol use disorders. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 2008;32(12):2149-2160.
(3) Miller, J.W., Naimi, T.S., Brewer, R.D., Everett Jones, S. Binge Drinking and Associated Health Risk Behaviors Among High School Students. Pediatrics Jan 2007, 119 (1) 76-85; DOI: 10.1542/peds.2006-1517
