Cardiovascular Health
- Cardiovascular Health Home
- CVH Data and Trends
- CVH Programs & Resources
- Minnesota 2035 Plan
- Minnesota Stroke Program
- About Us
Learn More
Related Topics
Contact Info
Cardiovascular Health Program
Cardiovascular Health Indicator
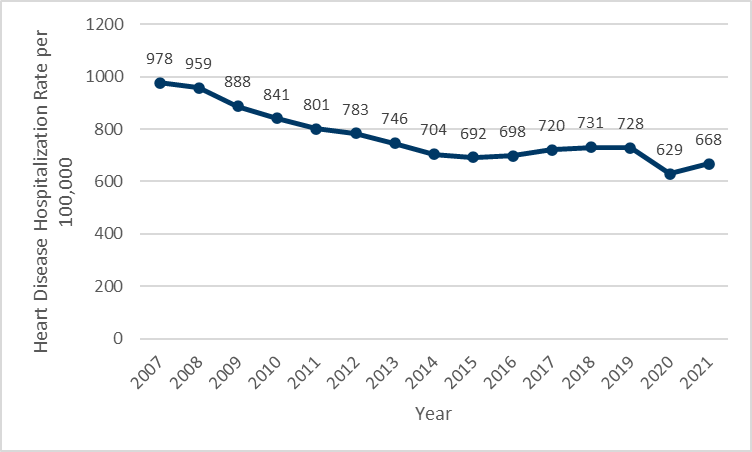
Measure: Heart Disease Hospitalization Rate
| Indicator | Date of Most Recent Measure | Current Measure | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age-adjusted hospitalization rate due to heart disease | 2021 | 668.1 per 100,000 |
Stable |
Overview
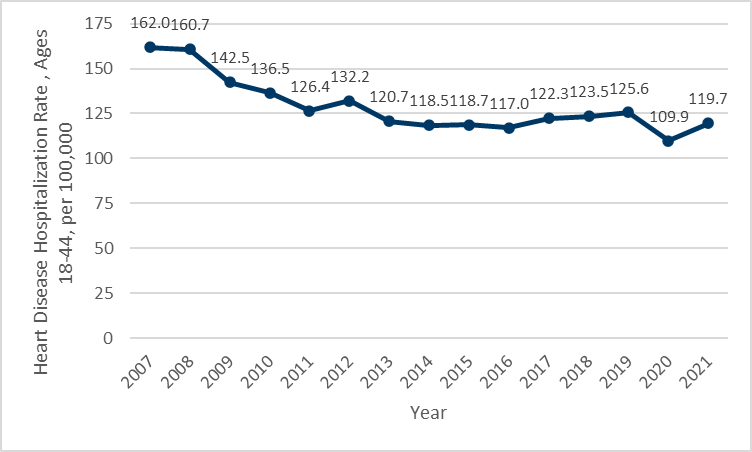
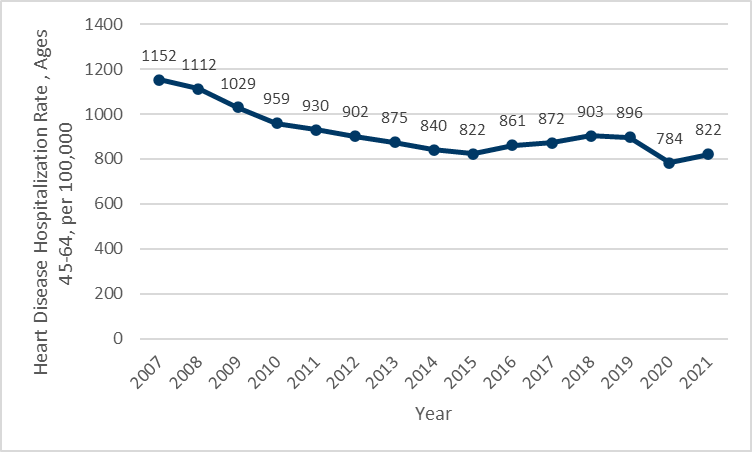
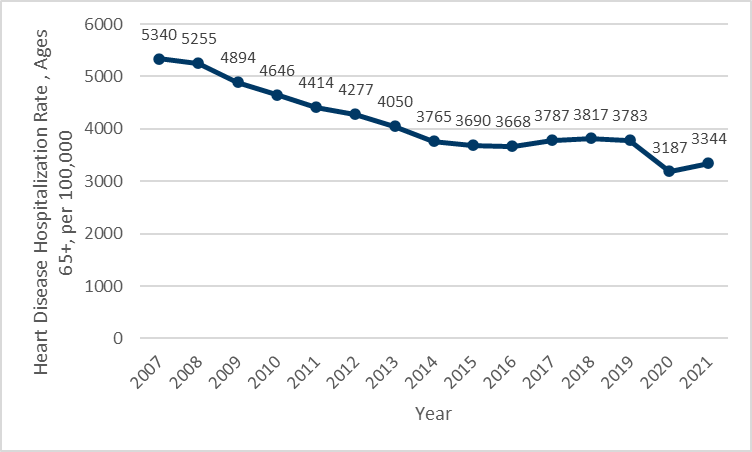
- In 2021, there were more than 46,000 hospitalizations of Minnesotans for heart disease, or a rate of more than 668 hospitalizations per 100,000 people.
- The total number of hospitalizations of Minnesotans due to heart disease declined through 2014, and rose by more than 14%, or more than 6,000 hospitalizations through 2019. In 2020, the number of hospitalizations declined sharply, a result of the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. Hospitalizations increased in 2021, back to levels last seen in 2016.
- Although the number of hospitalizations has risen, the average annual hospitalization rate since 2015 was essentially stable through 2019, rising approximately 5%. It is unclear if recent changes in hospitalization rates are a trend or are temporary impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic.
See Also:
Quick Facts about Heart Disease
Last Updated: 06/06/2023