Cardiovascular Health
- Cardiovascular Health Home
- CVH Data and Trends
- CVH Programs & Resources
- Minnesota 2035 Plan
- Minnesota Stroke Program
- About Us
Learn More
Related Topics
Contact Info
Cardiovascular Health Program
Cardiovascular Health Indicator
Measure: Blood Pressure Medication Adherence
| Indicator | Date of Most Recent Measure | Current Measure | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
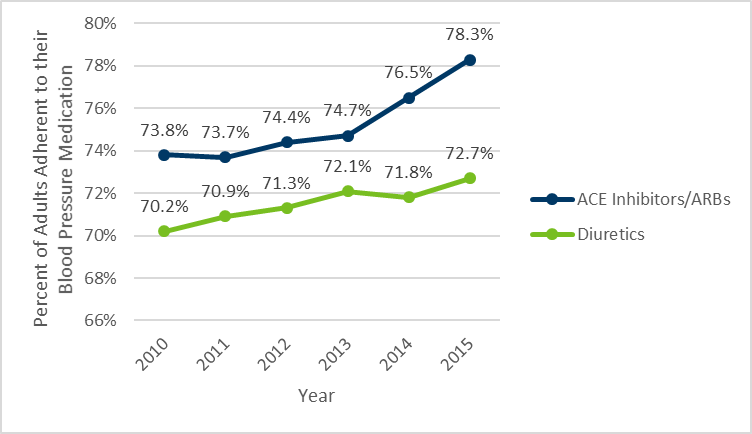
| Percentage of adults who are adherent to their antihypertensive medications | 2015 | ACE/ARB: 78.3% Diuretics: 72.7% |
Improving |
Overview
- In 2015, approximately 3 out of 4 Minnesotans taking blood pressure medications followed their doctor’s orders on taking the medications. Taking medications according to your doctor’s orders is associated with better control of high blood pressure.
- For one class of medications, ACE Inhibitors and ARBs, 78.3% of Minnesotans are adherent to their medications, a modest improvement since 2010.
- For a second class of medications, diuretics, a slightly lower percentage of Minnesotans (72.7%) are adherent to their medications, a slight improvement since 2010.
Last Updated: 01/03/2023