Children and Youth with Special Health Needs (CYSHN)
Programs
- Birth Defects Monitoring and Analysis
- Early Hearing Detection and Intervention
- Follow Along Program
- Longitudinal Follow-up for Newborn Screening Conditions
Related Sites
Contact Info
About the Children and Youth with Special Health Needs Section
Vision
A Minnesota where all children and youth with special health needs and disabilities can live a life of dignity, opportunity, joy, and belonging.
Mission
We work together to champion the health and well-being of Minnesotans with special health needs and disabilities from the earliest stages of life through transition to adulthood.
Strategic focus areas
- We are a transparent, efficient, and engaged section.
- We engage in strong, collaborative relationships that enhance and extend our mission.
- We design and implement programs while transforming systems to reduce health disparities and improve outcomes for children and youth with special health needs and disabilities.
- By leveraging our resources; increasing our capacity, learning, and growth; and committing to improved processes, we will meet the needs and expectations of our community and partners.
Who do we serve?
One in every five Minnesota families with children has at least one child with a special health need. Estimates of children with special health needs in Minnesota range from 160,000 to 200,000
Respect for identities
In our commitment to inclusivity and respect for all identities, we strive to use language that honors each individual’s preferences and lived experiences. We recognize that having a health condition or disability is a natural and valuable part of human diversity, and that language used to describe identity is both personal and evolving. For example, some people with disabilities prefer identity-first language (e.g., “disabled person”), others prefer person-first language (e.g., “person with a disability”). We respect these differences and aim to use descriptors relevant to the context and only when essential. We strive to stay responsive and open to changing our terminology as language evolves.
In alignment with federal and state statutory language, our program uses the term “special” in the title Children and Youth with Special Health Needs and Disabilities. We acknowledge that for some, the term “special” is considered problematic and may imply a sense of “otherness” rather than inclusion. While this language reflects current terminology, we remain open to exploring ways to address and evolve its usage in response to community feedback. Our goal is to communicate in ways that reflect each person’s preferred identity and foster a sense of belonging and respect.
Our approach to inclusive language emphasizes relationship-building, respecting each person’s chosen identity, and acknowledging that preferences can change over time. This statement serves as general guidance, as we understand that meaningful connection with individuals and communities is essential to fully respecting their identities.
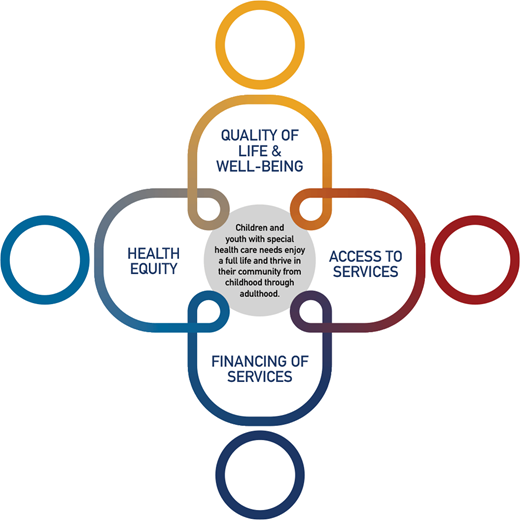
Families of CYSHCN are partners in decision making at all levels
CYSHCN receive coordinated, ongoing, comprehensive care within a medical home
Families of CYSHCN have adequate private and/or public insurance
Children are screened early and continuously for special health care needs
Services for CYSHCN are organized so families can use them easily and are satisfied with the services they receive
Youth with special health care needs receive the services necessary to make transitions to all aspects of adult life, including adult health care, work, and independence
References
- Conners Edgeworth, D., Boudreau, A. D., AlHajri, B., & Berry, J. G. (2022). Addressing health care inequities in children with medical complexity. Pediatrics, 149(Supplement 7), e2021056150C.
- Perrin JM, Romm D, Bloom SR, et al. A family-centered, community-based system of services for children and youth with special health care needs. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2007;161(10):933–935.