Commercial Tobacco Use
Tobacco Topics
- Behavioral Health and Commercial Tobacco
- COVID-19 and Commercial Tobacco
- E-cigarettes and Vaping
- Flavored Commercial Tobacco Products
- Menthol Commercial Tobacco Products
- Nicotine and Nicotine Dependence
- Secondhand Smoke and Aerosol
- Traditional and Sacred Tobacco
Related Topics
Contact Info
Tobacco NUMBRS
Tobacco and Nicotine Use in Minnesota: Briefs, Reports, and Statistics
Tobacco NUMBRS aims to increase the visibility and accessibility of data on commercial tobacco use in Minnesota. This page features a series of data briefs, among other resources like factsheets and reports, highlighting findings from various surveys of tobacco use and other data sources.
Click to subscribe for updates. We will send you new reports, data briefs, and other resources as they are released.
On this page:
Data briefs
Youth data
Adult data
Tobacco-related disparities
State and county data
Data briefs
The Hidden Harms of Menthol: Ending the Legal Sales of Menthol Commercial Tobacco Products would Advance Health Equity in Minnesota
March 2024
Menthol is more than a minty flavor in commercial tobacco products. Menthol’s cooling and numbing properties mask the harshness of commercial tobacco products, making them easier to use and more appealing. Tobacco companies know that flavors like menthol increase the odds that people, especially young adults and teens, will try their products and use them often enough to become regular users.
Menthol makes commercial tobacco products more appealing to new users and interacts with nicotine to make commercial tobacco products more addictive. Tobacco companies disproportionately market menthol products to Black, Native American, LGBTQ2+ communities, and young people. Ending sales of menthol and other flavored tobacco products would improve the health of Minnesota communities targeted by Big Tobacco and protect future generations from nicotine dependence.
More data briefs
- 11/15/2022: SHIP supports local Tobacco 21 policies, helping to reduce youth commercial tobacco use (PDF)
- 6/21/2022: Downward Trend in Adult Cigarette Smoking Continues (PDF)
- 5/12/2022: Minnesota Teens Vape Sweet and Minty Flavors (PDF)
- 3/24/2022: Minnesota Teens Prefer Commercial Tobacco Products with Flavors (PDF)
- 7/30/2020: Tobacco Control Efforts Save Minnesota Lives and Money (PDF)
- 7/30/2020: Vaping Erases 15 Years of Progress Lowering Youth Tobacco Use (PDF)
- 8/21/19: Tobacco Use and Asthma (PDF)
- 8/21/19: Smoking and Vaping around Youth who have Asthma (PDF)
- 2/4/19: Teen Tobacco Use in Rural Minnesota (PDF)
- 12/11/18: Which Minnesota Teens Try Vaping? (PDF)
- 10/31/18: Teen Vaping Initiation in Minnesota (PDF)
Statistics
Minnesota youth data
Any commercial tobacco use
- Current Use: 13.9% of high school and 3.7% of middle school students reported having used a commercial tobacco product in the past 30 days, a statistically significant decline from 20.5% (high school) and 4.1% (middle school) in 2017. An estimated 48,722 students in grades 6 through 12 used a commercial tobacco product in the past 30 days, 16,328 fewer than in 2020.
- Ever Use: 32.2% of high school and 12.0% of middle school students reported having ever used a commercial tobacco product, a statistically significant decline from 2020 among high school students (37.9% and 12.4%, respectively).
Source: Minnesota Youth Tobacco Survey, 2023
Flavored commercial tobacco use (e-cigarettes, little cigars, smokeless, hookah, and menthol cigarettes)
- Three in four students who have ever tried a commercial tobacco product initiated with a flavored product (76.3%).
- Among students who currently use commercial tobacco (past 30-day): 81.2% of students used a flavored product (menthol or other flavors) in the past 30 days.
- Among students that currently smoke (past 30-day): 38.8% of high school and middle school students reported having smoked a menthol cigarette in the past 30 days.
- Among students that currently use e-cigarettes (past 30-day): 93.3% of high school and middle school students reported having used a flavored (menthol or other flavored) e-cigarette in the past 30 days.
- Among students that currently use cigars (past 30-day): 38.4% of students reported having smoked a flavored (menthol or other flavored) cigar in the past 30 days.
- More than half of students that currently use smokeless commercial tobacco (e.g, chew) (past 30-day) reported having used a flavored product in the past 30 days.
Source: Minnesota Youth Tobacco Survey, 2023
E-cigarette use
- Current Use: 13.9% of high school and 2.2% of middle school students reported having used an e-cigarette in the past 30 days, a statistically significant decrease from 2020 among high school students (19.3% and 2.9%, respectively).
- Ever Use: 27.7% of high school and 7.7% of middle school students reported ever using an e-cigarette, a statistically significant decline from 2020 among high school students (35.4% and 7.9%, respectively)
Source: Minnesota Youth Tobacco Survey, 2023
E-cigarette and recreational marijuana use
- 14.5% of high school students reported having ever vaped marijuana, a significant decrease from 18.2% among high school students in 2020. 2.2% of middle school students reported having ever vaped marijuana, not statistically different from 2020 (2.5%).
- Among high school students who currently using e-cigarettes (past 30-day), 69.8% of high school and 51.4% of middle school students had ever vaped marijuana, a statistically significantly increase among high school students and a statistically significant decrease for middle students since 2020 (65.1% and 71.7%, respectively).
Source: Minnesota Youth Tobacco Survey, 2023
Signs of dependence
- 79.6% of students who used an e-cigarette in the past 30 days reported signs of e-cigarette dependence (87.7% of middle school and 78.7% of high school current e-cigarette users).
- 48.1% of current tobacco users reported having had a strong craving or feeling like they really needed to use a commercial tobacco product in the past 30 days.
- 49.5% of current e-cigarette users are frequent users (used on 20+ days in past 30), a significant increase from 2020 (33.6%).
Source: Minnesota Youth Tobacco Survey, 2023
Cigarette use
- Current Use: 4.5% of high school students reported having smoked a cigarette in the past 30 days (current smoking), not statistically different from 2020 (3.2%); 1.4% of middle school students reported current smoking, not statistically different from 2.0% in 2020.
Source: Minnesota Youth Tobacco Survey, 2023
Cigar and cigarillo use
- Current Use: 4.0% of high school students reported having smoked a cigar in the past 30 days (current use), statistically unchanged from 2020 (3.3%); 0.8% of middle school students reported current cigar use, not statistically different from the percentage in 2020 (1.1%).
Source: Minnesota Youth Tobacco Survey, 2023
Smokeless commercial tobacco use
- Current Use: 2.0% of high school students reported having used smokeless commercial tobacco in the past 30 days, statistically unchanged from 1.3% in 2020. 1.0% of middle school students reported having used smokeless commercial tobacco in the past 30 days, statistically unchanged from 2020 (0.9%).
Source: Minnesota Youth Tobacco Survey, 2023
Emerging nicotine and commercial tobacco products
- 5.2% of high school students reported having ever tried nicotine pouches; 3.0% ever tried nicotine gum, and less than 2 percent had ever tried nicotine-infused toothpicks, tablets/lozenges, or heated tobacco.
Source: Minnesota Youth Tobacco Survey, 2023
Youth access
- Among students that used an e-cigarette in the past 30 days (but could not legally buy commercial tobacco products) most commonly reported they got the e-cigarettes they used from social sources: 32.3% reported “someone offered them to me,” 18.2% reported they “asked someone to give me some,” and 21.9% reported “I bought them from another person.”
- 19.6% reported they bought e-cigarettes from a store (including online stores).
- 6.6% reported “my parents bought them for me” and 28.6% reported “I had someone other than my parents buy them for me.”
Source: Minnesota Youth Tobacco Survey, 2023
Quitting
- 68.5% of students who currently use commercial tobacco reported having intentions to quit within the next 30 days or later, while 31.5% reported they were not thinking about quitting.
- 65.4% of students who were currently using commercial tobacco reported having stopped using all commercial tobacco for one day or longer in the past year because they were trying to quit for good. Only 34.6% of students who are current commercial tobacco users reported not having tried to quit in the past year.
- 65.6% of students who currently use commercial tobacco and tried to quit did not use any source of help to quit, not even advice found on the internet.
Source: Minnesota Youth Tobacco Survey, 2023
Secondhand smoke
- 42.3% of middle and high school students reported they had been exposed to secondhand smoke during the past 7 days at one or more locations, a significant decrease from 2020 (46.9%).
- 27.9% of middle and high school students reported they had been exposed to secondhand smoke in an indoor or outdoor public place; 25.6% at work; 21.0% at school; 16.0% in a vehicle; and 15.0% at home.
Source: Minnesota Youth Tobacco Survey, 2023
Secondhand aerosol
- 30.0% of middle and high school students reported they had been exposed to secondhand aerosol during the past 7 days at one or more location, statistically unchanged from 2020 (28.3%).
- 15.0% of middle and high school students reported they had been exposed to secondhand aerosol in an indoor public place; 14.0% at home or in someone else’s home; and 11.6% in a vehicle.
Source: Minnesota Youth Tobacco Survey, 2023
Download this information: Data Highlights from the 2023 Minnesota Youth Tobacco Survey (PDF)
Minnesota Adult Data
Any Tobacco Use
- 20.8% use some type of tobacco product.
Source: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 2020
Cigarette Use
- Smoking fell to 13.8% (approximately 574,000 adults), a significant decrease from 2018 (15.1%).
Among 18-24 year olds
- Smoking nearly dropped in half from 14.0% in 2018 to 7.8% in 2020.
Source: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 2020
E-cigarette Use
- Overall e-cigarette use (used at least once in the past 30 days) has not changed since 2018 (5.0% in 2018 compared to 4.9% in 2020).
- The percent of adult e-cigarette users of all ages who are also current smokers declined significantly, from 44.8% in 2018 to 31.8% in 2020.
Among 18-24 year olds
- E-cigarette use did not change from 2018 (18.1%) to 2020 (18.2%) among young adults
- E-cigarette use exceeds cigarette use for this age group by a wide margin (18.2% vs. 7.8%).
Source: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 2020
Menthol Tobacco Use
- 27.5% report menthol cigarettes as their usual product
Source: Minnesota Adult Tobacco Survey, 2018
Quitting Tobacco
- • 50.5%, or 290,000 adult smokers, reported making a quit attempt in the past 12 months. This was a significant decrease from 54.9% in 2018.
Source: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 2020
Smokeless Tobacco Use
- • 3.7% of adults use smokeless tobacco compared to 4.1% in 2018—not a statistically significant change.
Source: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 2020
Tobacco Related Disparities
A complex set of factors has led to persistent health-disparities in the use and harm of commercial tobacco products between some groups.2 Disparities exist for several outcomes including:
- rates of commercial tobacco use
- exposure to secondhand smoke
- access to cessation support
- successful quit attempts
- exposure to commercial tobacco advertising and targeted marketing
Other commercial or social determinants of health also contribute to tobacco-related health disparities and can include key factors such as inequitable implementation and enforcement of tobacco control policies, social and environmental conditions that increase exposure to commercial tobacco products, structural racism and discriminatory practices, economic inequities, and access to education and job opportunities.2
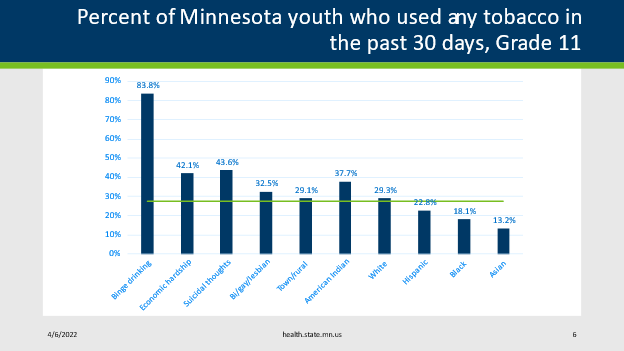
Source: Minnesota Student Survey, 2019; horizontal line represents statewide average of 27.6%.
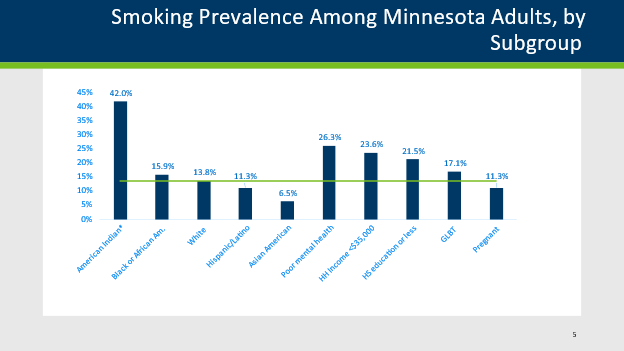
Source: BRFSS, 2020; horizontal line represents statewide average of 13.8%. *The smoking rate for American Indians obtained by BRFSS is relatively low compared to results of the Tribal Tobacco Use Project (TTUP) survey from 2013 (59.0%). TTUP is a larger, tribal-specific, statewide survey that is designed to produce a more accurate estimate for American Indians than BRFSS.
State and County Data
 Click below to view tobacco profiles for each of Minnesota's counties. These profiles show commercial tobacco's toll in each county in one year. They also include local and statewide data on products stores sell, youth tobacco use, and tobacco use during pregnancy.
Click below to view tobacco profiles for each of Minnesota's counties. These profiles show commercial tobacco's toll in each county in one year. They also include local and statewide data on products stores sell, youth tobacco use, and tobacco use during pregnancy.
More information
Reports
Minnesota Youth Tobacco Survey
The Minnesota Youth Tobacco Survey (MYTS) has been conducted since 2000, by the Minnesota Department of Health to provide comprehensive, in depth information on the tobacco use of young people and to design and evaluate prevention efforts. The MYTS is a representative sample survey. The eight MYTS was conducted in 2020, and previous surveys took place in 2000, 2002, 2005, 2008, 2011, 2014, and 2017.
- Report: Teens and Tobacco in Minnesota: Highlights from the 2020 Minnesota Youth Tobacco Survey (PDF)
- Report: Teens and Tobacco in Minnesota: Highlights from the 2017 Minnesota Youth Tobacco Survey (PDF)
Learn more about the Minnesota Youth Tobacco Survey.
Minnesota Student Survey
The Minnesota Student Survey (MSS) is conducted every three years among populations of Minnesota public schools. The census-like survey asks questions about activities, experiences, and behaviors. Topics covered include: tobacco, alcohol and drug use, school climate, physical activity, violence and safety, health, connections with school and family, and other topics.
The survey is administered jointly by the Minnesota Departments of Education, Health, Human Services, and Public Safety. The Minnesota Student Survey collects data by 5th, 8th, 9th, and 11th grades.
Learn more about the Minnesota Student Survey.
Minnesota Adult Tobacco Survey
The Minnesota Adult Tobacco Survey (MATS) is a collaborative effort between ClearWay Minnesota and the Minnesota Department of Health. MATS is the most thorough source of information about tobacco behaviors, attitudes and beliefs in Minnesota and helps measure the progress of Minnesota’s comprehensive tobacco control program. Previous MATS surveys were conducted in 1999, 2003, 2007, 2010, and 2014.
The 2014 MATS is a cross-sectional, random digit-dial telephone survey, conducted from February to July 2014 among adults aged 18 and older living in Minnesota. The sample of 9,304 responding adults consisted of 5,300 from a statewide landline sample and 4,004 from a cell phone sample.
Learn more about the Minnesota Adult Tobacco Survey.
Other Reports
For more information
- Tobacco Use Prevention: 2025 Report to the Minnesota Legislature (PDF)
- Tobacco Use Prevention: 2023 Report to the Minnesota Legislature (PDF)
- Tobacco Use Prevention: 2021 Report to the Minnesota Legislature (PDF)
- Tobacco Use Prevention: 2019 Report to the Minnesota Legislature (PDF)
- Tobacco Use Prevention: 2017 Report to the Minnesota Legislature (PDF)
- Minnesota Center for Health Statistics
![]() Interested in data on other topics? Visit the Minnesota Public Health Data Access portal.
Interested in data on other topics? Visit the Minnesota Public Health Data Access portal.
References
- Watkins, S.L., S.A. Glantz, and B.W. Chaffee, Association of Noncigarette Tobacco Product Use With Future Cigarette Smoking Among Youth in the Population Assessment of Tobacco and Health (PATH) Study, 2013-2015. JAMA Pediatr, 2018.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Identifying and Eliminating Tobacco-Related Disparities: Key Outcome Indicators for Evaluating Comprehensive Tobacco Control Programs—2022. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center forChronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health; 2021.
Trying to Quit Smoking, Vaping, or Chewing?
 Quit Partner is Minnesota’s family of programs to help people who want to quit smoking, vaping, chewing, or using other commercial tobacco products. Call 1-800-QUIT-NOW (784-8669) or visit Quit Partner.
Quit Partner is Minnesota’s family of programs to help people who want to quit smoking, vaping, chewing, or using other commercial tobacco products. Call 1-800-QUIT-NOW (784-8669) or visit Quit Partner.
For more help, visit Quitting Ccommercial Tobacco.